The GuideStar Method:
Aligning Leadership, Operations, and Performance
The GuideStar Method applies the same astronomical guide star concept to leadership, project management, and operations. It establishes a stable framework for clarity, alignment, and execution, ensuring that teams are high-performing and adaptable. By integrating Operational Excellence, Lean Methodology, and a Growth Mindset, the method enables:
- Clarity & Alignment – Defining a common approach to work and collaboration, keeping teams focused on strategic goals.
- Real-Time Adjustments – Continuously refining workflows to respond to change and improve efficiency.
- Predictability & Stability – Reducing inefficiencies and uncertainty through structured execution.
How the GuideStar Method Drives Performance
A high performing team isn’t just goal driven; it operates with a shared understanding of how work is approached and how team members interact. While company goals provide overall direction, they can sometimes be too broad or abstract for daily operations. To ensure alignment between strategy and execution, the GuideStar Method applies:
- Mission-Driven Functional Performance – Every function within an organization should have a mission and values that directly connect to company-wide goals. This makes high-level objectives more relevant to day-to-day work.
- Adaptive Execution – If misalignment emerges between team efforts and company objectives, leaders adjust workflows, priorities, or strategies to stay on course.
- Leadership as a Guiding Force – True performance isn’t just about setting goals—it’s about ensuring consistent alignment and execution across all levels of the organization. Leaders must reinforce focus, adaptability, and structured decision-making to maintain momentum.
Team leaders that exemplify GuideStar principles provide clarity and direction, empowering teams to navigate complexity and drive continuous improvement. Through strategic decision making and strong communication, they foster a culture of adaptability and long term success.
Leadership
Goal Setting Model
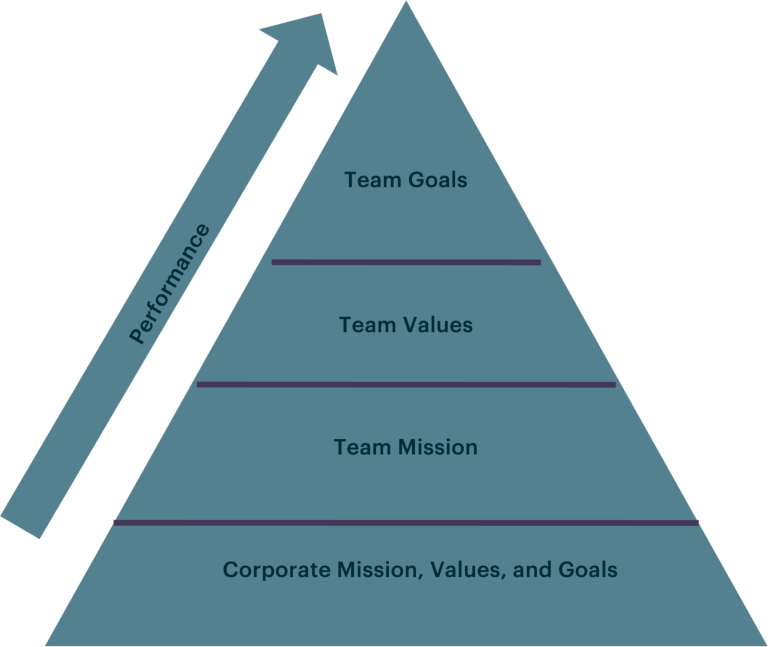
- A high performing team is rallied around a common understanding of how they approach their work and interact with others.
- Company goals are an imperative, but are sometimes too abstract and not directly relevant to immediate operations needs, for that reason we apply a mission statement and values to drive function performance. Therefore, it is critical for a team to create and own a mission and set of goals that supplement and build upon the foundation of the company’s overall direction.
- It is critical that the function's mission and goals always align with, and enable, the company's overarching Mission and Goal.
- Performance is a result of alignment and execution of all these driving forces.

Mission
What we aim to accomplish
Drive excellence in every facet of project management and Operations, aiming to seamlessly integrate cutting-edge technologies, streamlined processes, optimized resource utilization, and environmental sustainability. This will support efficient and reliable delivery of groundbreaking solutions to deliver on the promises of the people we help.
Values
These provide alignment with the core mission and provide a tactical way to steer the team toward a common purpose
Agility
Prioritize a nimble and adaptive approach, embracing flexibility in processes and systems to ensure our operations stay ahead of the curve
- Actively identify and address challenges swiftly, ensuring minimal disruptions and maintaining operational flow
- Embrace changes with a proactive mindset, adjusting plans and strategies as needed
- Continuously review and refine processes to improve daily operations
- Cross-train to foster a versatile workforce, allowing for smooth transitions during periods of increased demand or unexpected absences
Reliability
Meticulously planning and executing every aspect of our processes to deliver consistent and accurate results, fostering trust in both internal and external stakeholders.
- Adhere to protocols, ensure the accuracy and reliability of data, processes, and deliverables
- Thoroughly document and standardize processes to ensure transparency, accountability, and reproducibility
- Utilize tools to track operational metrics in real-time, allowing for immediate identification and resolution of any variation from established benchmarks
- Prioritize effective time management and coordination to ensure timely delivery of projects and operational milestones
Collaboration
Champion cross-functional collaboration to seamlessly communicate between functions and ensure a cohesive operational strategy
- Actively foster communication channels between functions and prevent silos through regular meetings, shared platforms, and collaborative tools
- Leverage diverse expertise for comprehensive problem-solving to develop holistic solutions to issues
- Ensure alignment and shared understanding of project and operational goals
- Host regular knowledge-sharing sessions to disseminate insights and expertise across teams, enhancing the collective intelligence of the organization
Optimization
Maximize resources through data-driven decision making and strategic management, minimizing waste to ensure lean, sustainable, and impactful work
- Leverage data insights to identify areas for optimization, guiding resource allocation to maximize efficiency and impact
- Integrate environmentally conscious practices into operations. From energy-efficient technologies to waste reduction, a commitment to sustainability aligns with resource optimization
- Proactively approach procurement through strategic negotiation, bulk purchasing, and seeking cost-effective alternatives. The team constantly evaluates suppliers to ensure the best value
- Collaboratively assess resource needs for upcoming projects, preventing underutilization or overallocation of resources.
Innovation
Explore and implement new technologies, methodologies, and efficiency measures to enhance our operational capabilities and maintain a competitive edge
- Seek out and advocating for the adoption of cutting-edge technologies remaining at the forefront of technological innovation
- Stay informed about industry trends and best-practices
- Contribute to ongoing process refinement through sharing positive and negative experiences
- Establish feedback loops with stakeholders to contribute insights on processes, informing improvements and evolving approaches
Guide the team’s individual actions and maintain the group's focus
Embody Mission & Values
PERFORMANCE
is an outcome of three attributes:
Results matter and are measured by the impact relative to company goals
Achieve Results
The biggest and most lasting impact is the result of helping others succeed
Servant Leadership
Coaching for Performance
A great coach does more than instruct—they inspire, empower, and develop people. Within our team, leadership at all levels should act as positive coaches, supporting skill development, accountability, and motivation while reinforcing operational excellence.
Building a high-performing team requires more than technical expertise—it requires a culture of trust, collaboration, and continuous learning. To foster this environment, we integrate key principles from the Positive Coaching Alliance (PCA), which emphasize team cohesion, growth mindset, and constructive feedback. These principles, commonly applied in coaching sports teams, are equally valuable in developing resilient and engaged professional teams.
By combining this alongside Lean and Agile methodologies, the team can build a culture of high performance, adaptability, and trust—critical for sustaining operational excellence in a growing company.

Team
Cohesion
Enhance respect & trust
- Establish Team Norms: Set clear expectations for communication, collaboration, and performance.
- Lead by Example: Managers and senior staff should model professionalism, accountability, and continuous learning.
- Encourage Peer Recognition: Use Agile standups or team meetings to highlight contributions and problem-solving efforts.
- Encourage collaborative problem-solving rather than top-down directives.
- Create peer recognition programs (e.g., "shoutouts" in meetings or project dashboards).

Growth
Mindset
Fill the "emotional tank"
- Balance Praise with Constructive Feedback: Use a 3:1 ratio (three positives for every critical piece of feedback).
- Develop Team Confidence: Recognize small wins and progress, not just final outcomes.
- Encourage Initiative: Give team members opportunities to lead initiatives or process improvements.
- Ask open-ended questions like “What’s working well for you?” and “What barriers are slowing you down?”
- Use daily or weekly check-ins to align, motivate, and empower the team.

Constructive Feedback
Prioritize learning & effort
- Effort Over Outcome: Encourage trying new solutions rather than fearing failure.
- Make Learning a Habit: Integrate Lean "Kaizen" (continuous improvement) practices.
- View Mistakes as Learning Opportunities: Use post-mortems constructively, not punitively.
- Provide specific, timely, and solution-focused feedback.
- Implement Lean-style feedback loops (e.g., real-time adjustments rather than waiting for performance reviews).
Team Cohesion & Feedback
Coaching & Development
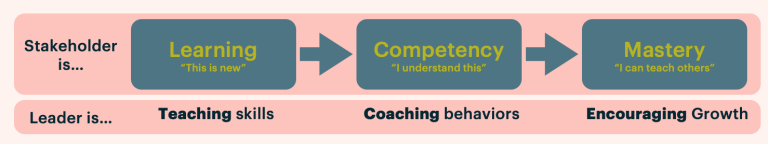
Teams and other stakeholders rarely, if ever, have all the skills mastered they need to truly excel at their role. Leaders must be proactive and intentional in growing their team’s skillset
Leaders must get their hands dirty, working closely with their teams
Creating a high-achieving team requires employees that feel uplifted, inspired, and supported to be their best. This requires the leader to meet the employee where they are at and be intentional with each interaction. Leaders must be comfortable with “getting their hands dirty” to support them in reaching their fullest potential. While supporting their team, a leader must always look for ways to remove roadblocks to allow people to achieve excellence
In order to make the biggest impact, leaders must:
- Know the Work - Get close to the work in order to recognize success and identify gaps
- Know the Person - Consider where a stakeholder is on their learning path in order to be guided correctly
- Know the Business - Understand what the company is trying to achieve to help the team see what’s possible and create plans for success
Be Genuinely Curious
Great leaders are deeply curious about their team’s development. A leader can generate deep insights by asking simple questions, and then interrogating reality in partnership with the employee.
- What are you trying to achieve?
- What’s your plan to get there?
- Where do we see evidence of your plan’s execution?
- What obstacles are there to execution?
Guide along a Learning Path
Great leaders take time to understand where someone is on their development path in order to meet them where they are to effectively, coach, encourage, and ultimately develop skills necessary for a project’s success. By working closely with the people on their team, leaders will be best positioned to grow the team’s capabilities.
GROWTH MINDSET
Maintaining a growth mindset during the scaling of operations is vital, as it promotes adaptability, resilience, and innovation—qualities necessary for navigating the complexities of growth.
By cultivating a growth mindset, operations teams can approach the challenges of scaling with confidence and creativity.
This mindset transforms obstacles into opportunities, enhances adaptability, and fosters a culture of continuous improvement, ensuring that the organization remains resilient and poised for long-term success.
Encourage teams to view challenges as opportunities, embracing feedback, and persist in the face of setbacks
Promote Adaptability to Change
- Embrace Change: View change as an opportunity for improvement, rather than a disruption.
- Experiment and Iterate: Be open to trying new methods and refining them without fear of failure.
Promote Problem-Solving and Innovation
- Think Creatively: Approach obstacles as opportunities to innovate, finding new solutions rather than relying solely on past methods.
- Collaborate Effectively: Foster a culture where diverse perspectives are valued and leveraged for solving complex problems
Enhance Leadership and Team Development
- Empowers Development: Encourages employees to take ownership of their professional growth, learn new skills, and expand their capabilities.
- Strengthens Leadership: Promotes a leadership style focused on coaching, mentoring, and helping teams reach their potential
Drive Continuous Improvement
- Proactive Learning: Teams actively seek out best practices, tools, and knowledge to improve their workflows
- Feedback Culture: Creates an environment where constructive feedback is embraced as a means of growth.
Execution
•Capture everything
•Clarify intent and specifications
•Prioritize what needs done
•Plan key milestones & next Steps
•Communicate with stakeholders
•Execute your plan
•Observe outcomes
•Record Wins
•Evaluate what can be better
•Identify how to elevate capabilities
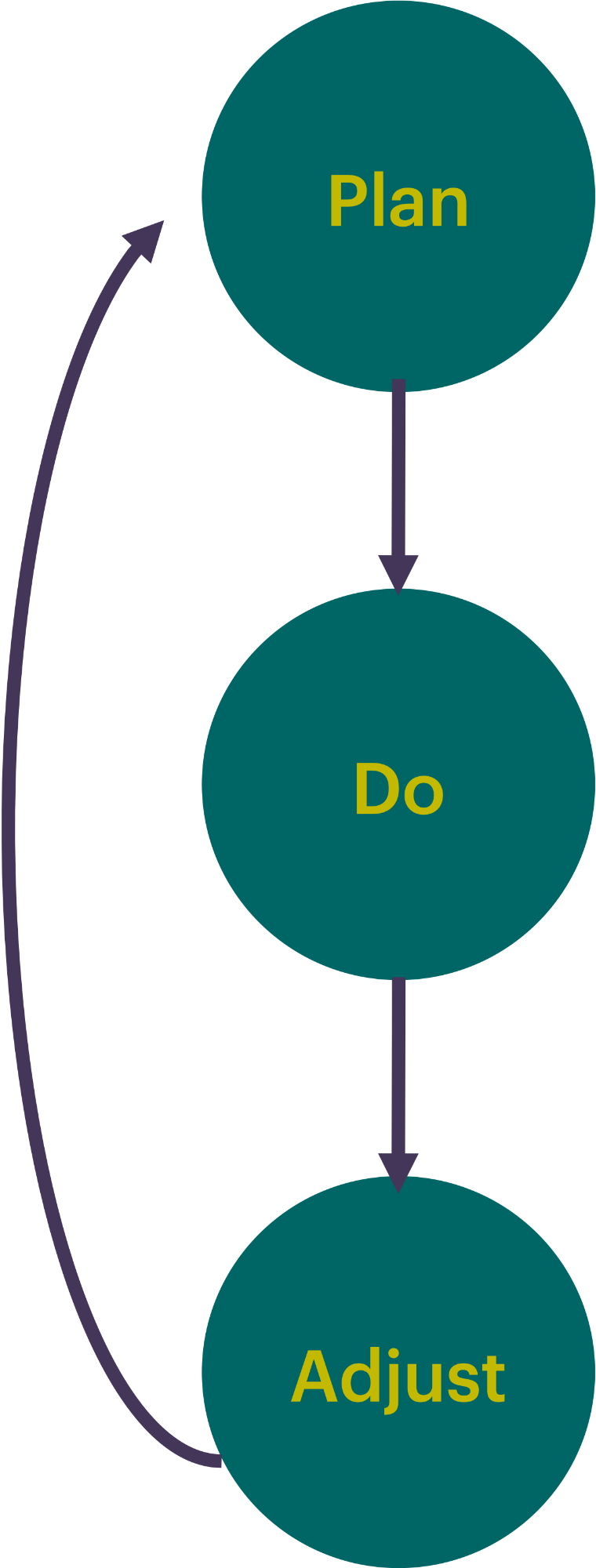
Operational excellence is not a static goal but a continuous journey. To ensure efficiency, adaptability, and ongoing improvement, utilize the Plan-Do-Adjust (PDA) cycle as a fundamental approach to executing and refining operations.
This ensures that teams remain proactive, adaptable, and committed to achieving predictable, high-quality results. Lastly, This methodology enables navigation of complex projects, regulatory requirements, and evolving business needs with confidence and precision
Plan
Start by clearly defining objectives, outlining necessary resources, and establishing measurable success criteria. Whether it's implementing a new workflow, managing procurement processes, or optimizing facility operations, careful planning ensures alignment with strategic goals while anticipating potential risks.
Do
Execution follows structured yet flexible action plans, emphasizing cross-functional collaboration and real-time problem-solving. During this phase, leverage appropriate project management principles to maintain focus, track progress, and adapt to operational challenges as they arise.
Adjust
Continuously evaluate outcomes using data-driven insights, stakeholder feedback, and performance metrics. Adjustments are made proactively to refine processes, eliminate inefficiencies, and enhance overall performance. This iterative approach, rooted in Lean and Growth Mindset principles, fosters a culture of continuous learning and operational resilience.
Leaders must seize opportunities to innovate and optimize team operations.
Excellence in day-to-day operations fuels the process of operational excellence and drives innovation and critical problem solving. Without a solid foundation of maintaining standards, innovation will fall flat and introduce issues, creating a backlog of festering problems. It is critical that new opportunities should be pursued after standards gaps are closed (i.e. we shouldn’t implement a new Chemical Inventory Management system when we don’t have a solid understanding of our chemical inventory and basic SDS).
Standard Gaps
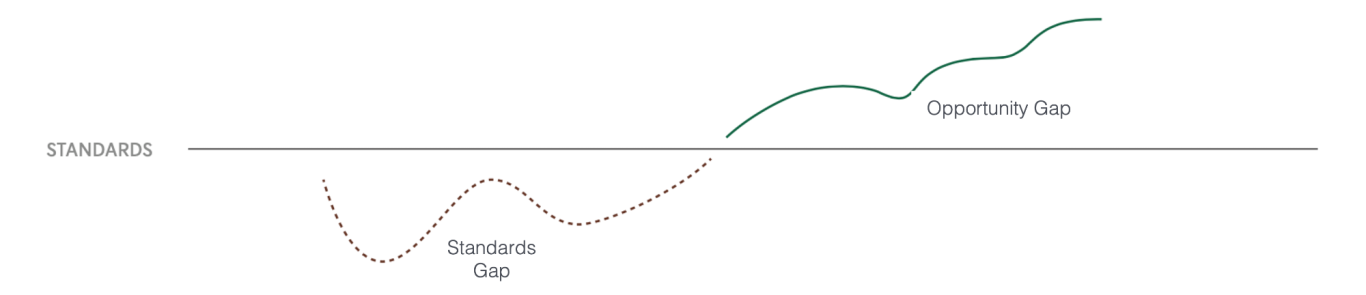
Standards gaps occur when basic company or compliance standards are not being achieved. These can create safety issues, legal headache, or otherwise negatively impact the company. They should always be treated with urgency.
Identify the necessary actions to return to standard and consider if processes or systems should be updated to avoid similar gaps in the future.
Opportunity Gaps
Opportunity Gaps represent a chance to capitalize on positive circumstances. This a chance for improvement, growth, or innovation and focuses on a specific area where positive change can occur. Evaluating opportunity gaps regularly allows the team to elevate the values of agility, reliability, collaboration,optimization, and innovation.
Plan for Scale
It is easy to get bogged down in the day-to-day work of operations. While it is important to provide uninterrupted services to stakeholders, we must always think about scaling work to match the needs as the organization grows.
General Principles:
- If an activity has more than a 70% likelihood of happening again, an SOP should be developed.
- Design workflows that can handle increased volume without sacrificing quality or compliance
- Implement scalable software and systems (e.g., ERP, LIMS, or project management tools) that can grow with the organization. Be especially considerate to systems than can add functionality as needed, reducing overall yearly OpEx
- Identify repetitive tasks that can be automated to increase efficiency
- Always be prepared for Change Management. Ensure leaders are ready to champion scaling initiatives. Clearly communicate changes and their purpose to all stakeholders. Finally, foster a culture that embraces change as an opportunity for innovation and improvement
- Talk about, encourage, and enable stakeholders to maintain a “Growth Mindset.” (see next page)
- Leverage Data for decision making
- Scenario Plan regularly
Implementing Systems & Tools
When a new system or tool is implemented, it can often risk disrupting work that is already performing well and delivering results. In general, the following principles should always be considered when working in an established environment:
- Abide by the KISS principle of (Keep It Simple, Stupid)
- Do not disrupt on-going healthy projects
- Bring unhealthy projects up to standards ASAP, but without additional timeline impacts
- Standardize and record tools quickly, even if imperfect
- Evolve intentionally (i.e. establish a yearly update interval for release of updated tools)
- Utilize and adapt pre-existing tools whenever possible (ex: DAI Decision Making Model)
- Emphasize cross-project collaboration
- Eliminate redundant work
- Minimize meetings, emphasize efficiency for those that must occur

Systems
Systems are the overarching structure that provides guidance, priority, and authority for moving the portfolio forward. These can be any number of interconnected processes that help us achieve business goals. A well designed system enhances communication, growth, and scalability.

Tools
Tools are any resource or application that helps perform tasks more effectively, efficiently, or accurately. They enable us to streamline operations, enhance productivity, clarify decision-making, and often provide an advantage by reducing errors or optimizing processes.

Change Management
Things are always changing, especially in a dynamic business environment. Everyone experiences change differently, and it is a leader’s job to move their team through change in order to continue achieving excellence.
The Knoster Model Change Equation helps us break down any change into its key elements. Working through the elements of the Change Equation should help you intellectually understand what the change means for you and your team.
It can also be a diagnostic tool. When working through change with your team, if you see any of the indicators on the right handside of the equation, you can track back what element partners may be missing
This tool is a starting point for large, complex change and isn’t always enough. It is ultimately the leader’s responsibility to help guide a team through changes, both big and small.

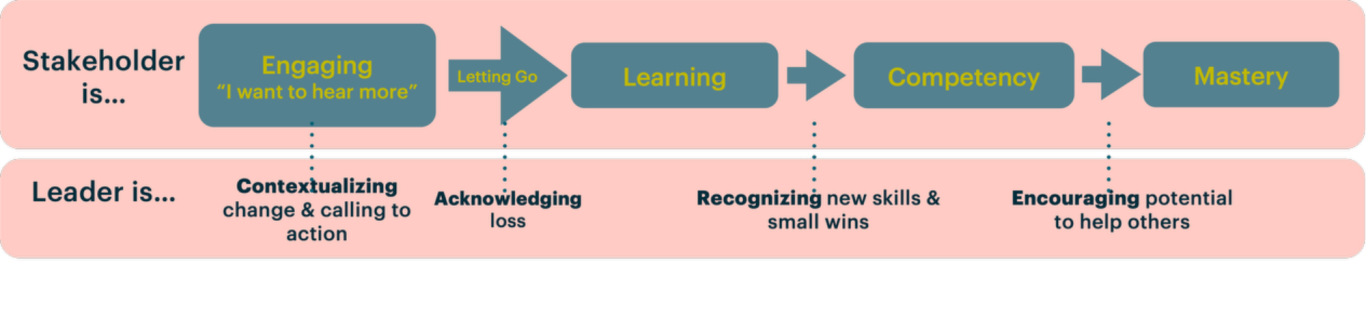
The Change Equation
Accepting Change
Ultimately, change is always a subjective experience. It is important to help a team embrace change personally. Often, this can mean people that were experts at something, or comfortable in the old ways of doing something are back to the “Learning” step of their learning path. Leaders must simultaneously support their team through the change, push for urgency, and allow space for their team to grow. It’s a fundamentally human process, but referencing the tools regularly can help in proceduralizing change management and providing a foundation of familiarity.
A leader’s role is to is to influence positive outcomes for the organization
- Carefully craft and deliver messages to move a task or project forward – thoroughly understanding the response you need to illicit and how different ones will affect your goals
- Consciously consider the message’s content, format, timing, and delivery method to make sure it “lands” appropriately
- Minimize misunderstandings and foster clarity in objectives
- Create opportunities for purposeful, deliberate, and targeted exchanges
- Promote active listening and encourage meaningful interactions
Intentional Communication
Enhance Collaboration
- Provide the appropriate forum to collaborate
- Convey respect, validate individuals' contributions, and foster a sense of psychological safety within the team
- When conflicts do arise, encourage open and respectful communication that allows team members to express their concerns and work toward resolution
Solve
Problems
- Ensure that expectations are clearly communicated, understood, and agreed upon by all parties involved
- Team members know what is expected of them, which reduces uncertainty and builds trust.
Manage Stakeholders
- Clear communication of roles, responsibilities, and deliverables creates a sense of reliability and accountability
- Intentional communication involves sharing both successes and failures openly. When team members celebrate successes together and openly discuss failures or challenges, it creates an atmosphere of trust
Mastery of these skill areas will elevate the team's capabilities:
Clarity & Conciseness
- Know exactly what you need done
- Eliminate ambiguity
- Provide unobstructed direction
Emotional Intelligence & Empathy
- Self Awareness: recognizing your own emotions, triggers, and style
- Empathy: understanding and considering others’ emotions and perspectives
Time,
Place,
Manner
- Timing can be an art and must be considered on a case-by-case basis
- Consider the most effective forum
- How you deliver a message can be more important than what you deliver
Meetings
Meetings are a double-edged sword in most organizations. They serve as a vital way to move business forward but often can devolve into time wasting moral killers that are remarkably expensive to the company. Much has been written about how to have effective meetings, yet these problems still exist- so there is certainly no panacea. However, a few principles can help keep meetings productive and efficient:

Right-Size
Have no more than 12 people in a meeting

Foster Safety
Create an environment where opposing voices are heard and arguments systematically evaluated

Membership
Make sure a wide perspective of stakeholder voices are present

Purpose
Have a good answer for the question “Why are we here”

Clarity
Have an agenda with a schedule and specify decisions that need made.
Spend & Budget Discipline
Managing spend is the single most important thing the Operations team can contribute. Often Operations has the single largest budget in the organization- especially during enterprise growth phases with significant CapEx investment.
Good spend disciple can be managed through four major buckets of work:
01
Foster a Cost-Conscious Culture
•Educate the Team: Train employees to understand the impact of operational costs and encourage cost-saving behaviors.
•Incentivize Savings: Reward teams or individuals who contribute to reducing costs without compromising quality.
•Encourage Ownership: Empower employees to take responsibility for managing budgets and identifying cost-saving opportunities.
02
Monitor Key Cost Metrics
•Track Operational KPIs: Regularly monitor key metrics such as cost per unit, labor efficiency, and resource utilization.
•Compare Actuals vs. Budgets: Use variance analysis to identify and investigate deviations from budgeted costs.
•Automate Monitoring: Leverage dashboards or analytics tools to provide real-time insights into costs and spending.
03
Standardize & Streamline Process
•Develop Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Ensure consistency and eliminate inefficiencies by standardizing workflows.
•Conduct Process Audits: Periodically evaluate processes to identify bottlenecks and opportunities for improvement.
•Adopt Lean Principles: Apply lean methodologies to eliminate waste, such as overproduction, waiting times, or redundant processes
04
Rigorous Budgeting Control
•Develop Detailed Budgets: Create granular budgets for operational activities, breaking down costs by department, function, or project.
•Implement Approval Workflows: Require approvals for high-value purchases to prevent unnecessary spending.
Centralize Procurement: Consolidate purchasing decisions to leverage economies of scale and negotiate better terms with suppliers
©Copyright. All rights reserved.
We need your consent to load the translations
We use a third-party service to translate the website content that may collect data about your activity. Please review the details in the privacy policy and accept the service to view the translations.